The S&P 500's price-to-earnings ratio (CAPE) has recently been nearing historic highs. Traders think that signals that market valuations might be overheated.
In December of last year, it hit 37.9, over double its long-term average of 17.6. For context, it has only exceeded that level during the Dot-Com bubble and in 2021.
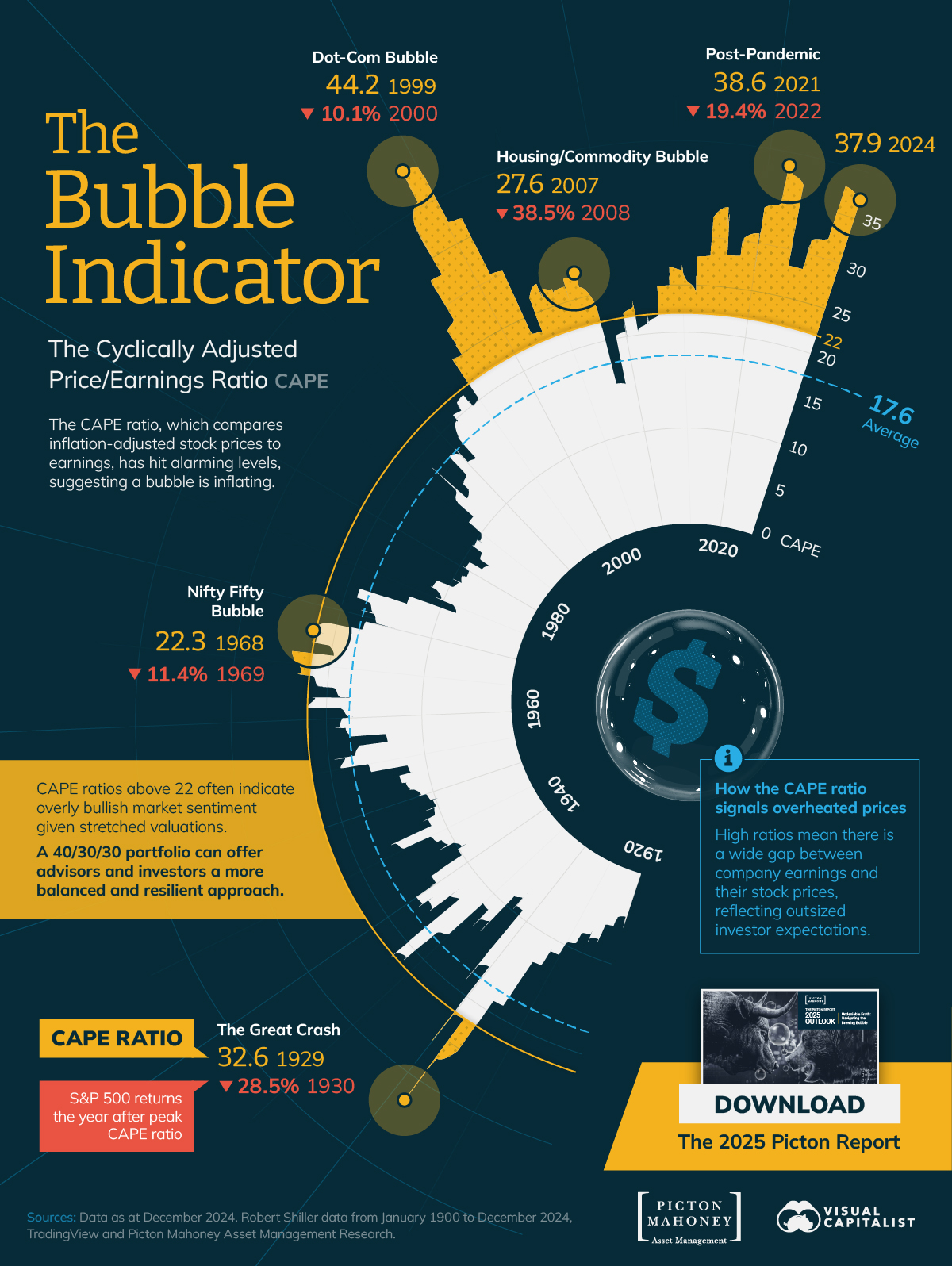
via visualcapitalist
Overheated prices mean that there's a significant gap between company earnings and stock prices. That disparity translates to speculation and hope driving the stock price instead of more quantitative data.
For some historical perspective, after the Dot-Com bubble, the S&P declined by 40% in the following two years. And after its 2021 peak, the S&P sank almost 20%.
While AI enthusiasm has brought a spark to the markets, the question is, is that hype hiding deeper issues?
On a broader note, my message to you would be that if you don't know what your edge is, you don't have one. Investors and traders should understand market indicators, economic trends, and other world factors – mainly because it's important to be educated (or at least informed). Of course, merely understanding these things does not translate to a reliable trading strategy or an edge in today's environment.
Lastly, just because something has been true in the past does not mean it predicts the future. In trading, we use the phrase "past performance is not indicative of future results" to remind us that there is a difference between a coincidence and a correlation. Indicators like CAPE study the past, so it is dangerous to assume you can use them to predict the future. For better or worse, whether markets go up or down is based on much more than earnings and stock prices.
But, with that said, Warren Buffett just did something worth noting … He sold his holdings in the S&P 500 index funds he tells everyone to buy. So why did Buffett just sell them himself?
We live in interesting times.
Onwards!

Leave a Reply