Trip Advisor has an interesting game called Traveler IQ Challenge.
I thought it was fun.
 On a related note, here are some of my favorite Travel sites.
On a related note, here are some of my favorite Travel sites.
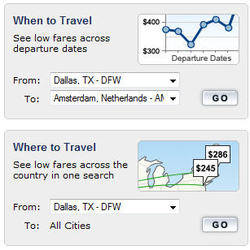
Farecast: This site has lots of nice features. This link shows cheap fares from a city. The graphic to the right shows other features to look for on that page. For example:
- when to travel (which days have the lowest fares), and
- where to travel (which cities have the best deals).
Kayak: Search 140+ travel sites at once to find and compare the cheapest fares from all sites together – great grids and filters to find what you are looking for fast.
Airfare Watchdog: Up-to-date list of low fares from major airlines (including Southwest). You can subscribe to alerts too.

Leave a Reply