Life expectancy has been on a steady global rise for longer than I've been alive.
via worldometers
Meanwhile ... the United States has fallen to 48th on the list of countries with the highest life expectancy.
Hong Kong tops the list with an average life expectancy of 85.63 overall - and 88.26 years for females.
For comparison, the U.S.'s average life expectancy is only 79.46.
Many factors potentially impact the findings, for example, the average height and weight of a population (with shorter & lighter people tending to live longer), diet, healthcare system, and work/life balance.
While some of this is out of your control (OK, a lot of it is) - there are definitely things you can do to increase your healthy lifespan. Meanwhile, some people like Bryan Johnson are doing everything they can to live forever.
Popular Mechanics put together a video series called How to Live Forever, or Die Trying, where they interview scientists and anti-aging gurus to give you insight into pursuing a future without death.
Unfortunately, recent science has shown that adults in their mid-40s to early 60s begin to experience significant changes in their alcohol, caffeine, and lipid metabolism, an increase in risk of cardiovascular disease, and a noticeable decrease in their skin and muscle health. When you hit your 60s, you also begin to see negative changes in carbohydrate metabolism, immune regulation, kidney function, and a further decline in the previously mentioned factors.
Here's the good news. Not only is science and technology getting better, but you're always in control. You can make lifestyle changes to increase your longevity, and you can also find supplements, treatments, and protocols that can reverse those factors of aging. Even simple measures like increasing your physical activity or avoiding alcohol before bed can make a massive difference.
They say a healthy person has thousands of dreams, but an unhealthy person only has one.
That is one of the reasons I spend so much time and energy thinking about staying healthy, fit, and vital.
Focusing on the positive is important ... But to extend your healthy lifespan, you have to start by telling the truth and finding out what you and your body struggle with the most.
A doctor friend gave me some advice. He said it doesn't matter if you are on top of 9 out of 10 things ... it's the 10th that kills you.
Despite our best efforts, Mother Nature remains undefeated.
With that said, here are some of my previous articles on longevity and health:
- Live Long & Prosper
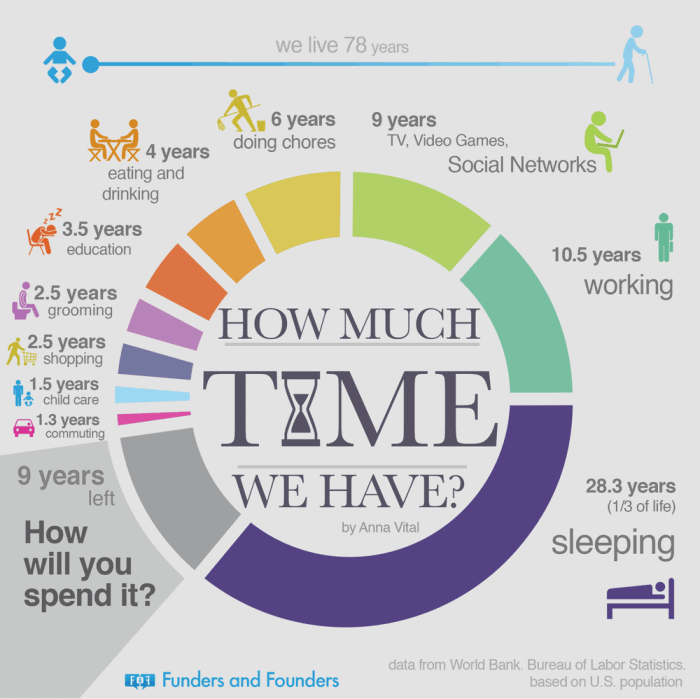
- How Much Time Do You Have Left?
- Changing Your Definition Of Resolution
- Workouts That Work
- Getting Used To A New Normal (Pt 1, Pt 2, Pt 3)
The goal isn't just to stay alive longer; it's to live life to its fullest for as long as possible.
I recently joined a fantastic mastermind group called DaVinci 50, run by Lisa and Richard Rossi. It brings together a remarkable collection of medical professionals and entrepreneurs focused on the latest research, treatments, and opportunities in health and longevity.
Another great tool I rely on is Advanced Body Scan. Early detection is crucial, but so is tracking the history of your scans to monitor changes over time. In my opinion, the most valuable scan is always the next one.
Additionally, I use a growing list of trackers and biometric devices to measure my heart rate, along with apps and tools for mindfulness, breathwork, and journaling. Together, these practices recognize that mind, body, and spirit combine to define how you live your life.
To end this post, I'll use a farewell phrase I heard often while growing up ... it translates roughly to "go in health, come in health, and be healthy." It's a beautiful way to wish someone well on their journey, emphasizing the importance of health and well-being.
I hope you found something interesting. Let me know what things and practices work best for you.
Don't Walk Out On A.I. Just Yet
Amazon's 'Just Walk Out' technology has revolutionized shopping convenience, but whispers suggest there might be more to it than meets the eye...
For years, shoppers have been able to walk into one of their Amazon Fresh grocery stores, walk out, and never have to talk to a single person, or even check out.
This feat was supposedly made possible solely using machine intelligence.
However, they just announced that they're removing technology from their stores and switching to smart shopping carts.
Along with that announcement came rumors that the technology only worked due to a team of 1000 out of India. Apparently, this team was required to verify orders and correct the technology when it missed items.
On the one hand, that seems like a classic case of overpromising and underdelivering, but it's also very common. Many public-facing AI systems rely on human moderators and data labelers.
So why is Amazon being flogged in the media?
The problem for me is two-fold.
First, Artificial Intelligence is at the peak of inflated expectations on Gartner's Hype Cycle. That means the average user has high hopes and is being disappointed. It also means the average user is likely overwhelmed with apps and technologies that fail to deliver on their promises.
Second, transparency is the name of the game, especially in a black-box situation like most AI. The technology Amazon is creating is impressive—but they're also Amazon. Eyes are on them to be leaders, so when they fall short, it's a chance for naysayers to pile on.
Public perception is likely to trend downward in the next news cycle, which is to be expected. After the peak of inflated expectations comes the trough of disillusionment.
Regardless, AI will continue to become more capable, ubiquitous, and autonomous. The question is only how long until it affects your business and industry.
While Amazon has "walked out" on that technology in its stores, it's not time to "walk out" on AI just yet. Numerous stores still use that or similar technologies.
Posted at 09:00 PM in Business, Current Affairs, Food and Drink, Gadgets, Ideas, Market Commentary, Science, Trading, Trading Tools, Web/Tech | Permalink | Comments (0)
Reblog (0)