A few weeks ago, I shared an article about a tool I've been enjoying called Dot. I use it as an AI journal that acts somewhat like a sounding board and counselor for me.
Since writing that article, I have continued to enjoy and appreciate the tool. I've used Dot to help me plan and prepare for a substantial business transaction. It assists me in processing and evaluating significant life decisions. Sometimes, I even use it just because I'm bored.
Dot sometimes responded to my thoughts with probing questions which pushed me to consider why I said what I said. These prompts helped me think about my thinking in ways that I hadn't before. The result was more valuable than simply coming up with a strategy or a list of potential answers. It actually helped me articulate and identify what I really wanted.
It's clear to me that I increasingly rely on the tool and have made it part of my daily routine. I've even noticed that I sometimes refer to it as "she" or "her."
Dot remembers my discussions with it, prompts me to stick with things we've discussed, and can even tell when I'm trying to change the subject or end a conversation.

It's fascinating to think about how AI creates a programmatic version of empathy. It makes me question the distinction between artificial and real empathy (and whether that distinction even matters). Perhaps, instead, we should focus simply on the utility and benefits of the responses.
If you're into comparisons, you might want to check out Pi, one of the pioneering personal AI tools designed to blend EQ and IQ.
If you like variety, try Poe, developed by Quora. It gives you access to the latest AI models and millions of user-created AI chatbots and even lets you create your own custom bots.
I'm also a fan of TalkTastic, which lets you record your rough ideas and then distill them into thoughtful and articulate language. I use it frequently throughout the day to create short messages, emails, and even some of the sentences in articles like this. As I use voice more, I love the idea of a digital editor that declutters and refines what I say into what I mean.
Things Are Getting Better Fast!
As a thought experiment, imagine how advanced AI will be by the end of your lifespan.
Assign the number 100 to that level of capability. Where are we now?
Based on my life expectancy, I would guess that AI is currently only at a 3 out of 100.
Where we are today is incredible compared to the past. Likewise, it's astounding how fast things are getting better. But compared to what's coming … it's virtually nothing.
The most exciting part is that (considering the rapid pace of exponential technological improvements) we likely can't even imagine how advanced AI will become or the benefits and insights it will be capable of producing for us.
While my first article focused on the tool and its capabilities, I think it's also helpful to think more globally about mindsets around these types of tools and the proliferation of AI.
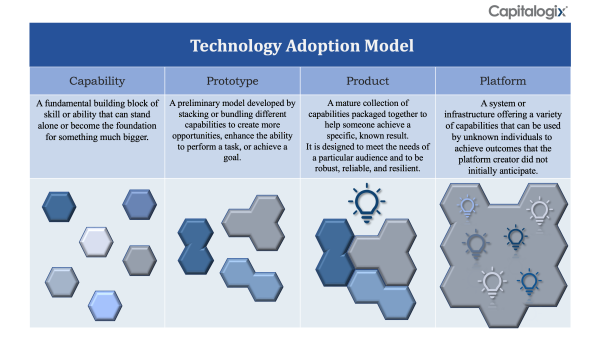
Technology Adoption Model
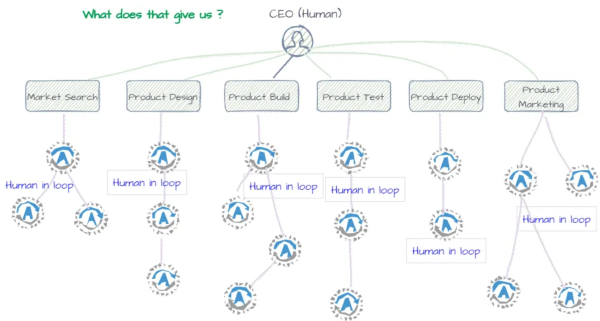
To start, I've built a model I call the Technology Adoption Model. This model explains how ideas transform from a Capability into a Product and then once again into a platform that spawns new capabilities.
Before you start considering new capabilities, the first thing you should do is assess whether this new tool helps us better accomplish what we already do. To answer that, we often use three simple measures: efficiency, effectiveness, and certainty. This means getting things done in less time, with less effort, or with a greater chance of success.
Once you know that you can do what you already did—just better—you naturally get greedy for more. That means you start thinking about what you could or should do to improve further.
This applies to adopting new tools – and also to building them.
I've also built a worksheet around the model that you can use in your own business.

As you start using new AI tools, you will gain new capabilities. Don't concentrate on mastering the tool itself; instead, focus on getting better at using it to enhance your life.
A great place to start is simply making your life easier or more enjoyable. Use new tools in fun and low-friction ways. The impact of tools like these will increase as you become more proficient at thinking about using them better … and as you improve your ability to imagine new possibilities.
From Inconceivable To Unavoidable
Your mindset creates your reality.
It's natural to feel resistance to new and powerful capabilities. It's a safety mechanism because humans are wired to think locally and linearly – and to avoid danger.
Realize, however, that linear thoughts don't often lead to exponential results.
The more I play around with these tools, the more I anthropomorphize them. Human thought and connection are ultimately chemicals and electricity firing within a system, not too different from a computer. If AI can become such a reasonable facsimile that it's indistinguishable, is the difference worth thinking about? Or is it better to focus on what and how you will use the new capabilities?
As entrepreneurs, our job is to get the rock up that hill. We can spend time thinking about whether the tool is 'artificial' or how we can better harness it.
I've said this before, but it's worth echoing … Some of what was once Impossible becomes Possible. Some of what became Possible becomes Probable. And, and some of what became Probable becomes Inevitable. Here is a way to visualize that scale.

And, our limitations are often only in our ability to conceive of a bigger future.
Speed Matters
AI isn't just valuable because of what it can do; its deeper value comes from enabling you to achieve more.
I like to use a simple model to illustrate this: Crawl, Walk, Jog, Run, Sprint. As you think about your day or week, what percent of the time are you sprinting?
Chances are you sprint less than you initially thought. Why? Because, when you really sprint, it's hard to breathe … and you can't talk. And because of all our other burdens and responsibilities, we don't tend to push ourselves that hard.
However, as AI eliminates frustration and bother, it frees you up to do and be more and focus on the things that create the most value and really matter.
The real benefit of AI is that it gives you back those time cycles to really sprint towards what you truly want.
A tool like Dot can also help you better clarify what you want while also helping you accomplish those things.
Too much of our day is spent thinking about what we don't want or how to avoid feeling angry, frustrated, or uncertain.
Your life can improve quickly by focusing on becoming more clear about what you want, how you can achieve it, and the best ways to measure progress toward those goals.
The next step is to use the traction, progress, and momentum to determine what else is possible and what you should plan to do next.
When you think about it this way, a tool like Dot can be a powerful alignment tool and a way to help you and your company move faster.
Just make sure you're heading in the right direction!











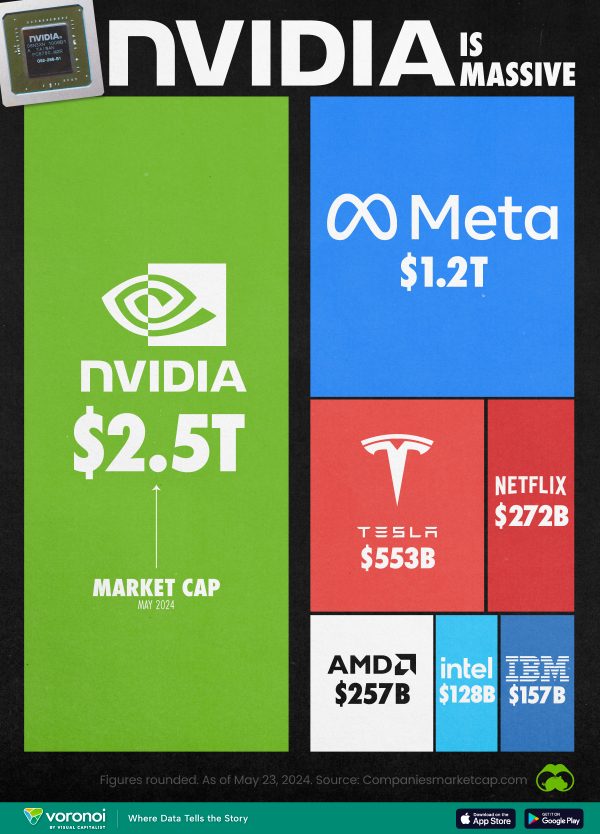 via
via 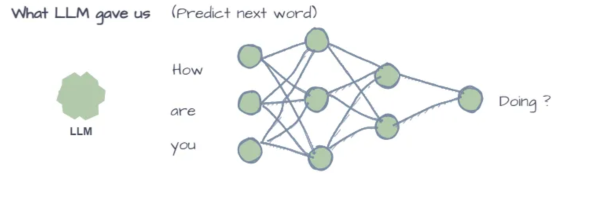
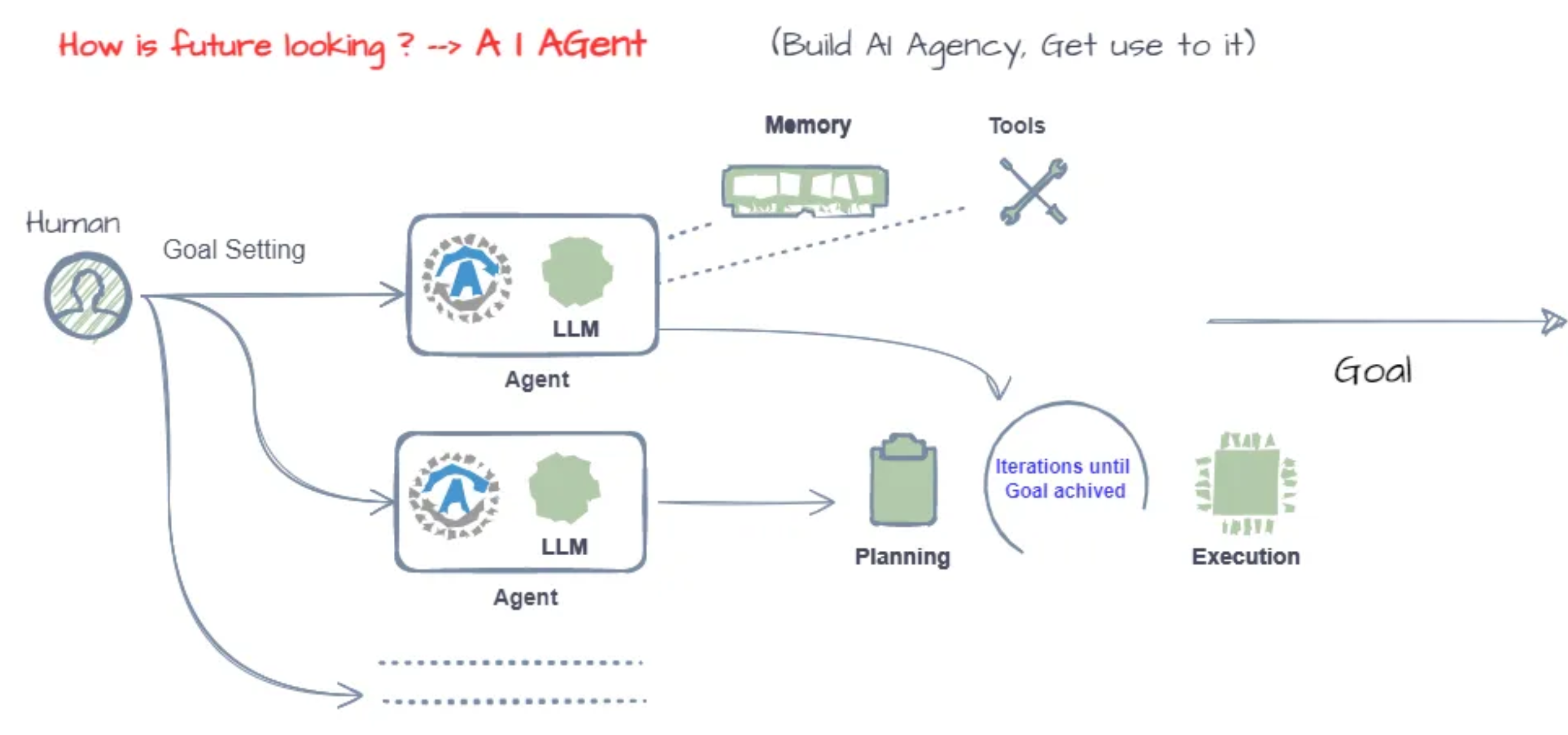 via
via