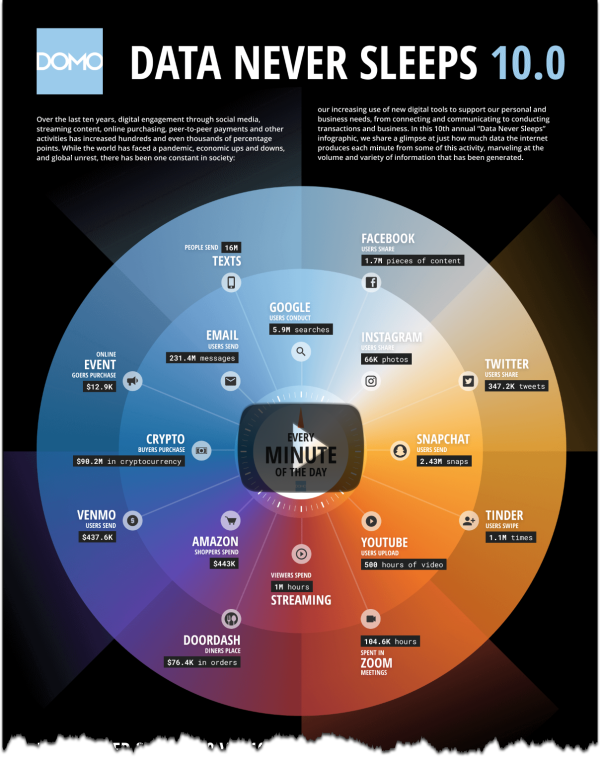
The Gartner Group’s Hype Cycle research provides the raw material for some of my favorite posts every year.
It is a graphical and conceptual presentation used to represent the maturity, adoption, and social application of popular technologies.
Here is a link to a Gartner research note on understanding Hype Cycles.
I’ve found that they are an excellent source of well-researched tech and business analysis. As another example, here is a video of their Top Ten Tech Trends for 2024.
via YouTube
Humans are famously bad at predicting the future of technologies. We tend to overestimate technology’s abilities in the near term and massively underestimate what it can do in the long term.
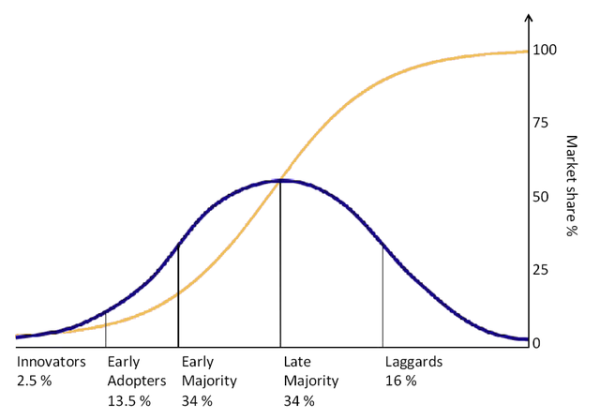
The shape of that curve has come to be known as the Gartner Hype Cycle, and the five stages of that curve are important for any entrepreneur or investor to understand.
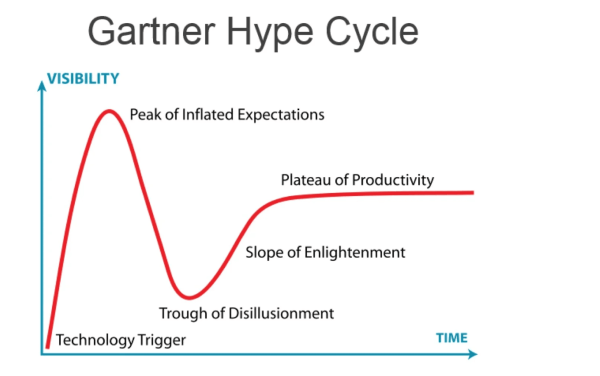 via Gartner
via Gartner
In general, as technology advances, it is human nature to get excited about the possibilities and disappointed when those expectations aren’t met.
At its core, the Hype Cycle tells us where we are in the product’s timeline and how long it will likely take the technology to hit maturity. It attempts to tell us which technologies will survive the hype and have the potential to become a part of our daily lives.
Gartner’s Hype Cycle Report is a considered analysis of market excitement, maturity, and the benefit of various technologies. It aggregates data and distills more than 2,000 technologies into a succinct and contextually understandable snapshot of where various emerging technologies sit in their hype cycle.
Here are the five regions of Gartner’s Hype Cycle framework:
- Innovation Trigger (potential technology breakthrough kicks off),
- Peak of Inflated Expectations (Success stories through early publicity),
- Trough of Disillusionment (waning interest),
- Slope of Enlightenment (2nd & 3rd generation products appear), and
- Plateau of Productivity (Mainstream adoption starts).
Understanding this hype cycle framework enables you to ask important questions like “How will these technologies impact my business?” and “Which technologies can I trust to stay relevant in 5 years?”
If you are curious, here is Perplexity’s explanation of Gartner’s Hype Cycle and related research.
Another methodology uses frequency analysis to identify the “most hyped” concepts and technologies.
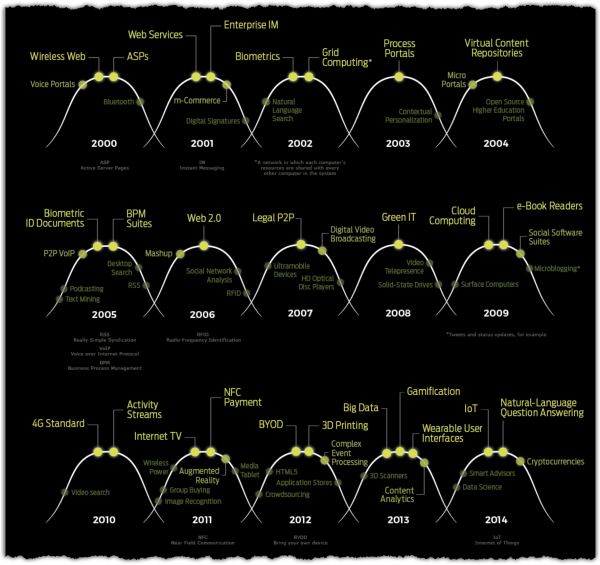
VisualCapitalist recently put together an infographic highlighting the most hyped technologies of each year. They call it the “Peak of Inflated Expectations”.
(Click To See Full Infographic) via VisualCapitalist
Here’s a Summary of the most hyped technologies, by year, since 2000.
- 2000 – Wireless Web, ASPs, Bluetooth
- 2001 – Web Services, Enterprise IM, m-Commerce
- 2002 – Biometrics, Grid Computing
- 2003 – Process Portals
- 2004 – Micro Portals, Virtual Content Repositories
- 2005 – P2P VOIP, Biometric ID Documents, BPM Suites
- 2006 – Mashup, Web 2.0
- 2007 – Legal P2P, Digital Video Broadcasting
- 2008 – Green IT
- 2009 – Cloud Computing, e-Book Readers, Social Software Suites
- 2010 – 4G Standard, Activity Streams
- 2011 – Internet TV, NFC Payment, Augmented Reality
- 2012 – BYOD, 3D Printing, Complex Event Processing
- 2013 – Big Data, Gamification, Wearable User Interfaces
- 2014 – IoT, Natural-Language Question Answering, Cryptocurrencies
- 2015 – Speech-To-Speech Translation, Advanced Analytics, Autonomous Vehicles
- 2016 – Blockchain, Cognitive Expert Advisors, Machine Learning
- 2017 – Virtual Assistants, Connected Home, Deep Learning
- 2018 – Biochips, Digital Twin, Deep Neural Networks
- 2019* – 5G, AI PaaS, Graph Analytics
*Missing from the infographic, but updated by Gartner
As we take our smartphones for granted, it’s hard to imagine Bluetooth, wireless web, or e-book readers as emerging technologies at this point – but at one point in time, the lightbulb was an emerging technology.
It’s also interesting to look at which technologies peaked in a hype cycle … and which now popular technologies no longer appear on this list. For example, despite Virtual Reality being around since the 80s, I still expected to see it on this list.
Cryptocurrencies, “smart homes”, and several older examples are in a recession – but that doesn’t mean they won’t have resurgences.
As a reminder, the hype cycle and the innovation adoption cycle are often on very different time scales. It’s very possible that technologies from the early 2000s may still have their heyday.
What are you surprised wasn’t on the list? And, what do you think is about to get added?
We live in interesting and exciting times!


 via
via