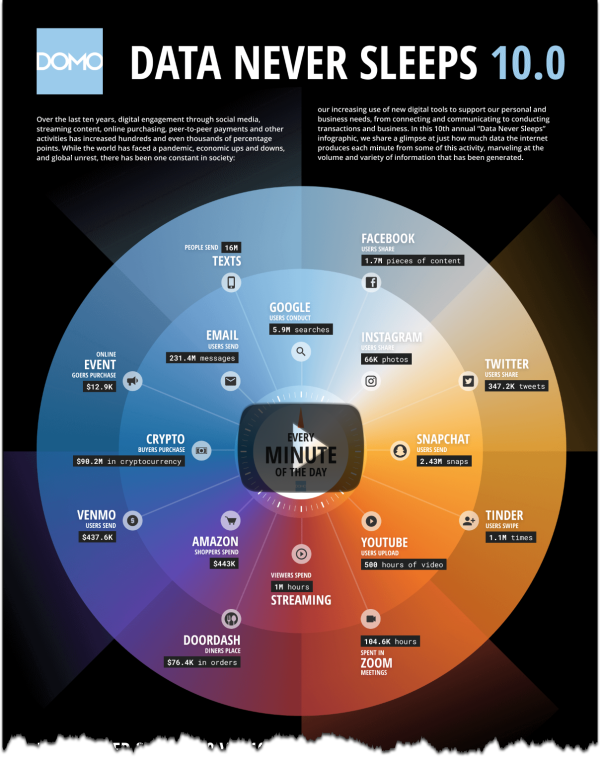
Are you Happy?
What does that mean? How do you define it? And how do you measure it?
Happiness is a surprisingly complex concept comprised of conditions that highlight positive emotions over negative ones. And upon a bit of reflection, happiness is bolstered by the support of comfort, freedom, wealth, and other things people aspire to experience.
Regardless of how hard it is to describe (let alone quantify) … humans strive for happiness.
Likewise, it is hard to imagine a well-balanced and objective "Happiness Report" because so much of the data required to compile it seems subjective and requires self-reporting.
Nonetheless, the World Happiness Report takes an annual look at quantifiable factors (like health, wealth, GDP, and life expectancy) and more intangible factors (like social support, generosity, emotions, and perceptions of local government and businesses). Below is an infographic highlighting the World Happiness Report data for 2025.
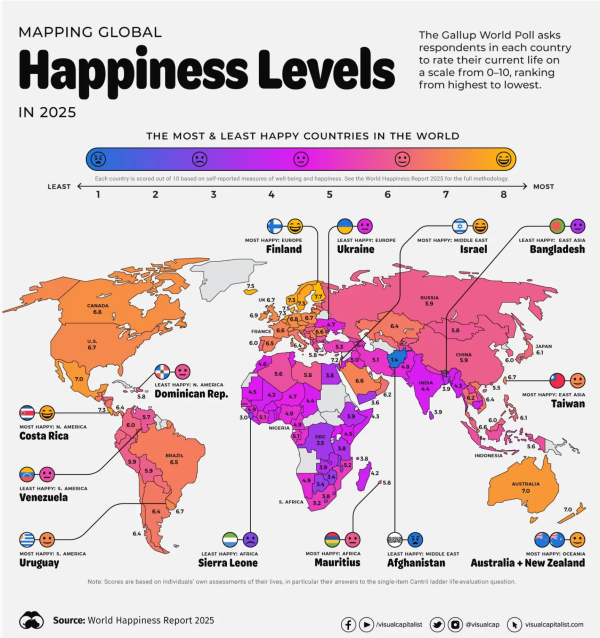
World Happiness Report via Gallup
Click here to see a dashboard with the raw worldwide data.
I last shared this concept in 2022. At the time, we were still seeing the ramifications of COVID-19 on happiness levels. As you might expect, the pandemic caused a significant increase in negative emotions reported. Specifically, there were substantial increases in reports of worry and sadness across the ninety-five countries surveyed. The decline in mental health was higher in groups prone to disenfranchisement or other particular challenges – e.g., women, young people, and poorer people.
Ultimately, happiness scores are relatively resilient and stable, and humanity persevered in the face of economic insecurity, anxiety, and more.
While scores in North America have dropped slightly, there are positive trends.
The 2025 Report
In the 2025 report, one of the key focuses was an increase in pessimism about the benevolence of others. There seems to be a rise in distrust that doesn't match the actual statistics on acts of goodwill. For example, when researchers dropped wallets in the street, the proportion of returned wallets was far higher than people expected.
Unfortunately, our well-being depends on our perception of others' benevolence, as well as their actual benevolence.
Since we underestimate the kindness of others, our well-being can be improved by seeing acts of true benevolence. In fact, the people who benefit most from perceived benevolence are those who are the least happy.
"Benevolence" increased during COVID-19 in every region of the world. People needed more help, and others responded. Even better, that bump in benevolence has been sustained, with benevolent acts still being about 10% higher than their pre-pandemic levels.
Another thing that makes a big difference in happiness levels worldwide is a sense of community. People who eat with others are happier, and this effect holds across many other variables. People who live with others are also happier (even when it's family).
The opposite of happiness is despair, and deaths of despair (suicide and substance abuse) are falling in the majority of countries. Deaths of despair are significantly lower in countries where more people are donating, volunteering, or helping strangers.
Yet, Americans are increasingly eating alone and living alone, and are one of the few countries experiencing an increase in deaths of despair (especially among the younger population). In 2023, 19% of young adults across the world reported having no one they could count on for social support. This is a 39% increase compared to 2006.
Takeaways
In the U.S., and a few other regions, the decline in happiness and social trust points to the rise in political polarisation and distrust of "the system". As life satisfaction lowers, there is a rise in anti-system votes.
Among unhappy people attracted by the extremes of the political spectrum, low-trust people are more often found on the far right, whereas high-trust people are more inclined to vote for the far left.
Despite that, when we feel like we're part of a community, spend time with others, and perform prosocial behavior, we significantly increase perceived personal benefit and reported happiness levels.
Do you think we can return to previous levels of trust in the States? I remember when it felt like both parties understood that the other side was looking to improve the country, just with different methods.
On a broader note, while we have negative trends in the U.S., the decrease is lower than you might expect. The relative balance demonstrated in the face of such adversity may point towards the existence of a hedonic treadmill - or a set-point of happiness.
Regardless of the circumstances, people can focus on what they choose, define what it means to them, and choose their actions.
Remember, throughout history, things have gotten better. There are dips here and there, but like the S&P 500 … we always rally eventually.
Onwards!

 via
via 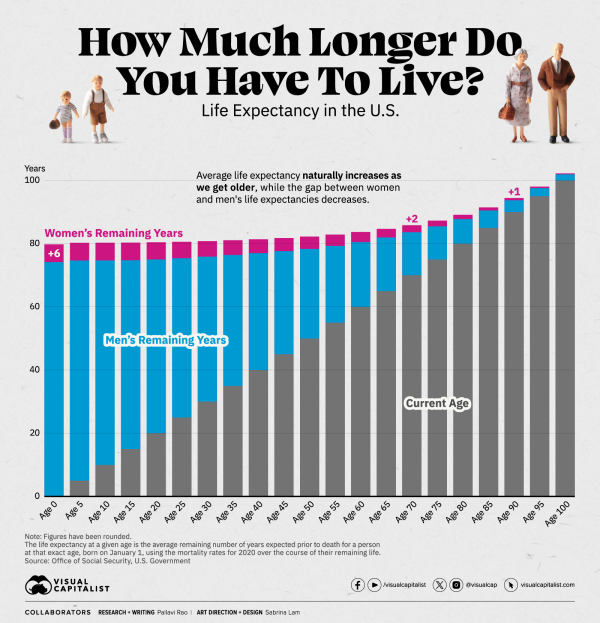








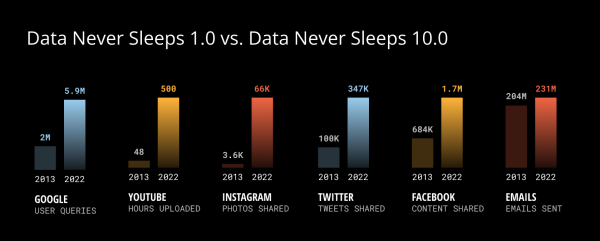 via
via