Each year, I share an article about Gartner's Hype Cycle for Emerging Technologies. It's one of the few reports that I make sure to track every year. It does a good job of explaining what technologies are reaching maturity, but which technologies are being supported by the cultural zeitgeist.
Technology has become cultural. It influences almost every aspect of every-day life, and it's also a massive differentiator in today's competitive landscape.
Sorting through which technologies are making real waves (and will impact the world) and which technologies are a flash in the pan, can be a monumental task. Gartner's report is a great benchmark to compare reality against.
2019's trends lead nicely into 2020's trends. While there have been a lot of innovations, the industry movers have stayed the same – advanced AI and analytics, post-classical computing and communication, and the increasing ubiquity of technology (sensors, augmentation, IoT, etc.).
What's a "Hype Cycle"?
As technology advances, it is human nature to get excited about the possibilities and to get disappointed when those expectations aren't met.
At its core, the Hype Cycle tells us where in the product's timeline we are, and how long it will take the technology to hit maturity. It attempts to tell us which technologies will survive the hype and have the potential to become a part of our daily life.
Gartner's Hype Cycle Report is a considered analysis of market excitement, maturity, and the benefit of various technologies. It aggregates data and distills more than 2,000 technologies into a succinct and contextually understandable snapshot of where various emerging technologies sit in their hype cycle.
Here are the five regions of Gartner's Hype Cycle framework:
- Innovation Trigger (potential technology breakthrough kicks off),
- Peak of Inflated Expectations (Success stories through early publicity),
- Trough of Disillusionment (waning interest),
- Slope of Enlightenment (2nd & 3rd generation products appear), and
- Plateau of Productivity (Mainstream adoption starts).
Understanding this hype cycle framework enables you to ask important questions like "How will these technologies impact my business?" and "Which technologies can I trust to stay relevant in 5 years?"
That being said – it's worth acknowledging that the hype cycle can't predict which technologies will survive the trough of disillusionment and which ones will fade into obscurity.
What's exciting this year?
Before I focus on this year, it's important to remember that last year Gartner shifted towards introducing new technologies at the expense of technologies that would normally persist through multiple iterations of the cycle. This points toward more innovation and more technologies being introduced than in the genesis of this report. Many of the technologies from last year (like Augmented Intelligence, 5G, biochips, the decentralized web, etc.) are represented within newer modalities.
It's also worth noting the impact of the pandemic on the prevalent technologies.
For comparison, here's my article from last year, and here's my article from 2015. Click on the chart below to see a larger version of this year's Hype Cycle.
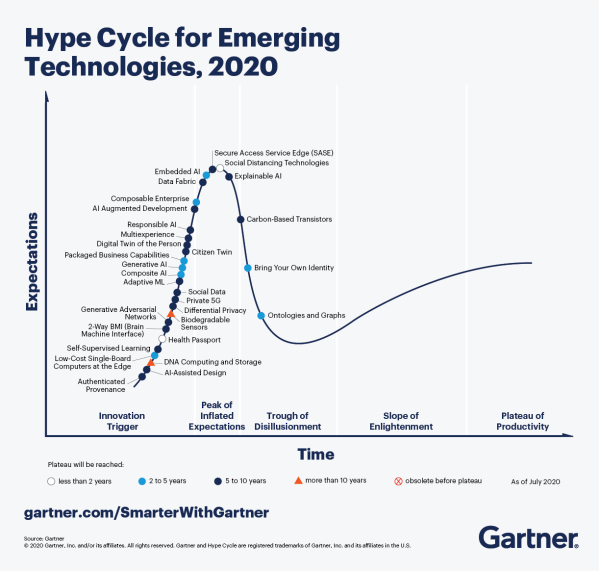
via Gartner
This year's ~30 key technologies were selected from over 2000 technologies and bucketed into 5 major trends:
- Composite Architectures represent the organizational shift to agile and responsive architectures due to decentralization and increased volatility. Emphasis is on modularity, continuous improvement, and adaptive innovation to respond to changing market conditions (like in trading, or in businesses rapidly shifting to remote). Sample technologies include embedded AI and private 5G
- Algorithmic Trust is a direct result of increasing data exposure, fake news, and biased algorithms. As a result, technologies have been built to "ensure" identities, privacy, and security. A great example is more technologies being created on the blockchain. Other examples include explainable AI and authenticated provenance
- Beyond Silicon is in its infancy, but represents the limitations of Moore's law and the physical of silicon. This has led to new advanced materials with enhanced capabilities being used, and other simple materials being used. Examples of this technology can be seen in DNA computing and storage, quantum computing, and biodegradable sensors.
- Formative AI is the shift towards more responsive AI; models that adapt over time and models that can create novel solutions to solve specific problems. Sample technologies include generative AI, self-supervising learning, and composite AI.
- Digital me represents the integration of technology with people, both in reality and virtual reality. Past hype cycles have introduced implants and wearables, but the potential applications of the technology are growing, especially in response to social distancing. Examples are health passports, Two-way BMI, and social distancing technologies.
I'm always most interested in the intersection of AI and advanced analytics. This year, it looks like many of the fledgling AI technologies have become integrated and more advanced. Much like the formative years for children, formative AI represents a new era in AI maturity. Models are becoming more generalized, and able to attack more problems. They're becoming integrated with human behavior (and even with humans as seen in digital me).
As we reach new echelons of AI, it's actually more likely that you'll see over-hype and short-term failures. As you reach for new heights, you often miss a rung on the ladder… but it doesn't mean you stop climbing. More importantly, it doesn't mean failure or even a lack of progress. Challenges and practical realities act as force functions that forge better, stronger, more resilient, and adaptable solutions that do what you wanted (or something better). It just takes longer than you initially wanted or hoped.
To paraphrase a quote I have up on the wall in my office from Rudiger Dornbusch … Things often take longer to happen than you think they will, and then they happen faster than you thought they could.
Many of these technologies have been hyped for years – but the hype cycle is different than the adoption cycle. We often overestimate a year and underestimate 10.
Which technologies do you think will survive the hype?



 via
via  via
via 
 via
via  via
via